
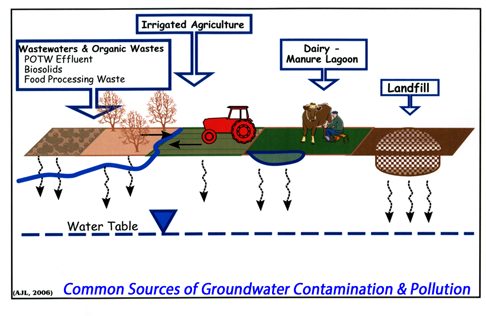
Evaluation, Protection, Monitoring & Regulation
Once Polluted, Groundwaters Are Very Difficult, If Not Impossible,
to Restore for Reliable Water Supply
 |
|
|
Evaluation, Protection, Monitoring & Regulation Once Polluted, Groundwaters Are Very Difficult, If Not Impossible, to Restore for Reliable Water Supply 
| |
![]() Return to G. Fred Lee & Associates Home Page
Return to G. Fred Lee & Associates Home Page